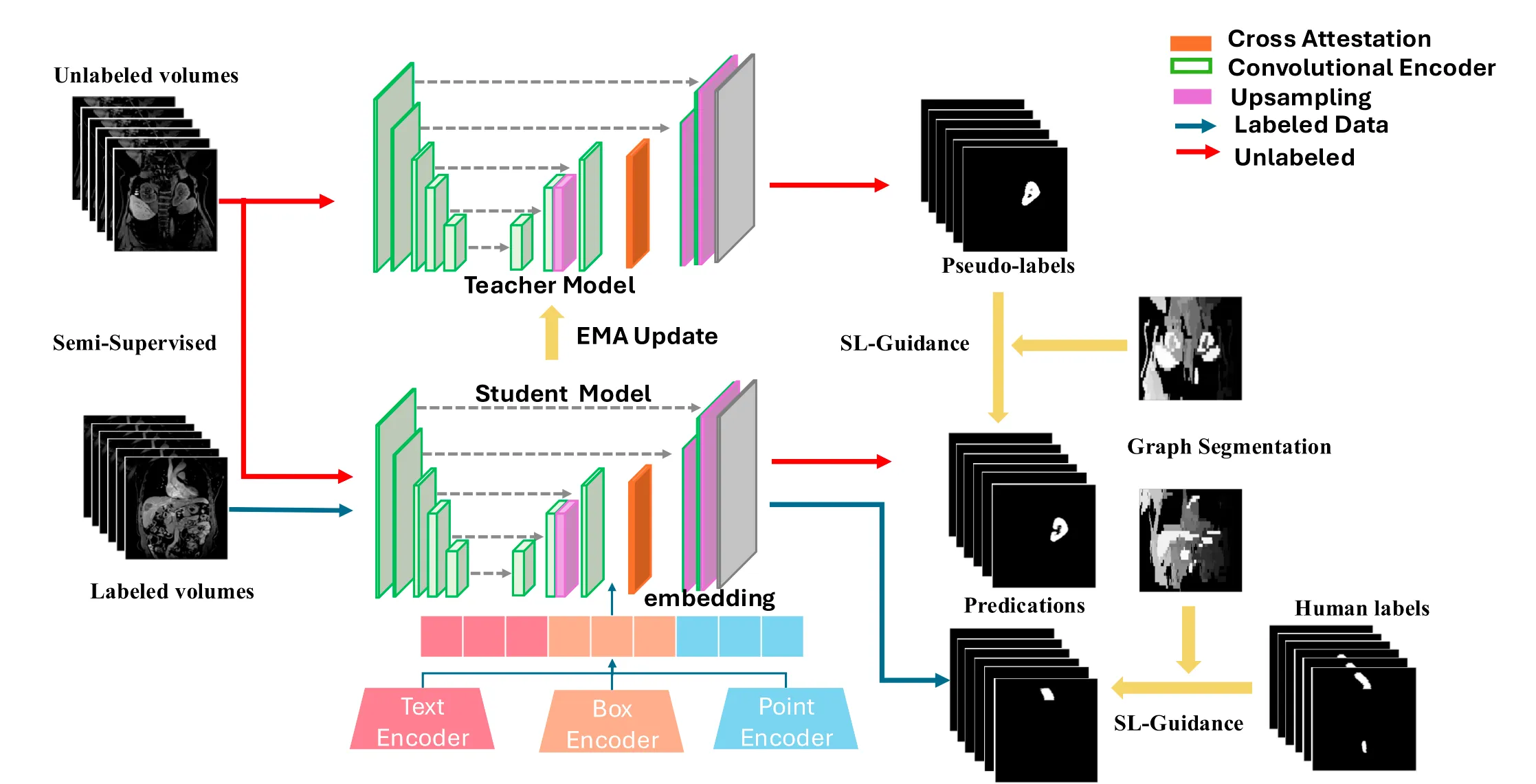
Clinical magnetic‑resonance (MR) protocols generate dozens of T1 and T2 sequences whose visual appearance differs more than the acquisition sites that produce them. Existing domain‑generalization benchmarks focus almost exclusively on cross‑center shifts and overlook this dominant source of variability. Pancreas segmentation remains a major challenge in abdominal imaging: the gland is small, irregularly shaped, surrounded by stomach, duodenum and visceral fat, and often suffers from low T1 contrast. State‑of‑the‑art deep networks that already achieve >90% Dice on the liver or kidneys still miss 20–30% tissue on the pancreas. In addition, the organ is systematically under‑represented in public cross‑domain benchmarks—even though accurate pancreas delineation is critical for early cancer detection, surgical planning and diabetes research. To close this gap, we present PancreasDG, a large-scale multi-center 3D MRI pancreas segmentation dataset specifically designed to investigate domain generalization in medical imaging. The dataset comprises 563 MRI scans from six institutions, spanning both venous phase and out-of-phase sequences, enabling systematic study of both cross-center and cross-sequence variations with pixel‑accurate pancreas masks created by a double‑blind, two‑pass protocol. Through comprehensive analysis of this dataset, we reveal three critical insights: (i) limited sampling introduces significant variance that may be mistaken for distribution shifts, (ii) cross-center performance correlates with source domain performance for identical sequences, and (iii) cross-sequence shifts present fundamentally different generalization challenges requiring specialized solutions. We further propose a semi-supervised learning approach for cross-sequence generalization that leverages anatomical invariances, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art domain generalization techniques with +61.63% Dice score improvements (from 43.55% to 70.39%) and +87.00% (from 35.62% to 66.61%) on two independent test centers for cross-sequence segmentation. PancreasDG establishes a new benchmark for domain generalization in medical imaging with implications beyond medical applications. Dataset, code, and models will be available after the peer-review process.
